publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2022
-
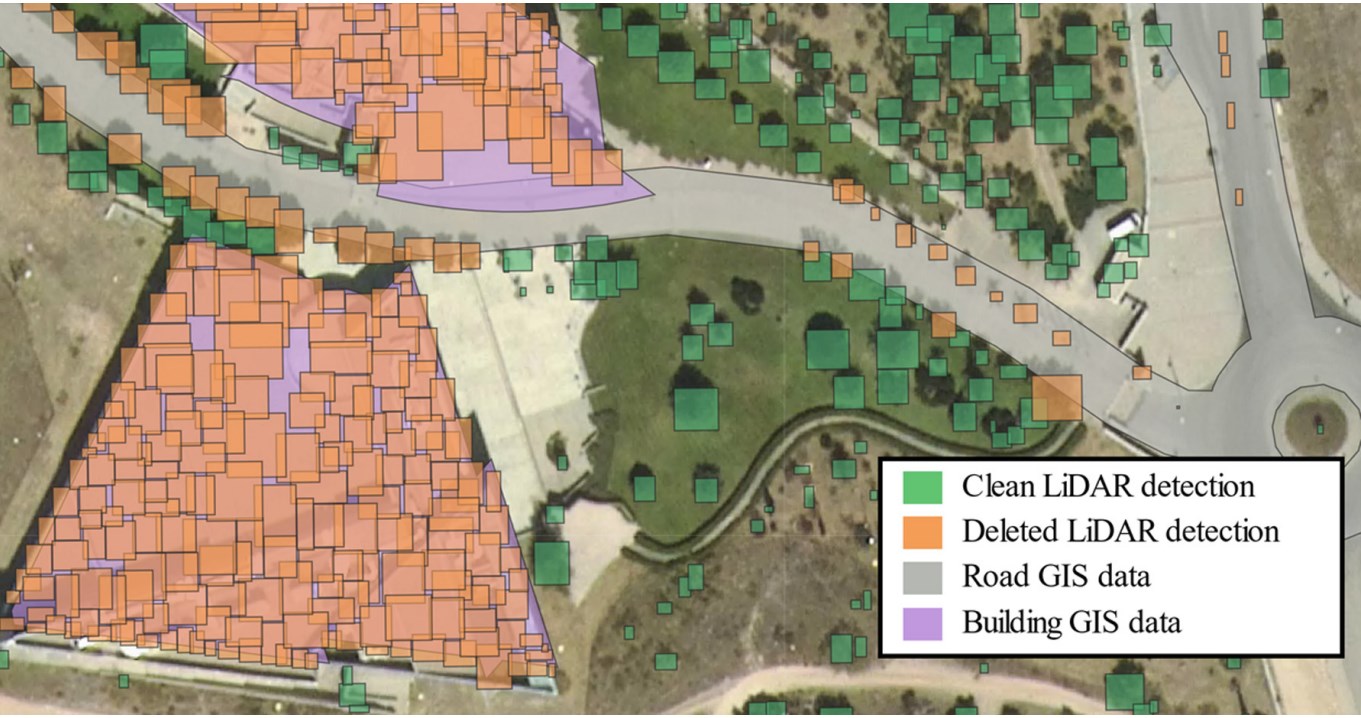 SOCO21
Automatic Individual Tree Detection from Combination of Aerial Imagery, LiDAR and Environment ContextAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 16th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2021) 2022
SOCO21
Automatic Individual Tree Detection from Combination of Aerial Imagery, LiDAR and Environment ContextAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 16th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2021) 2022Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow analysis based on geo-referenced data. Currently only simple geo-referenced information is available, such as road networks or types of terrain, but there are other geo-referenced data that would be very useful to facilitate decision-making. These data are not collected as they are very hard to generate manually, but remote sensing data and artificial intelligence can be used to accomplish it. This work aims to develop an automatic framework for the extraction of geo-referenced trees, through the union Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) point clouds, aerial imagery, and existing GIS environment context. The results of the process are satisfactory, improving in some several areas the LiDAR-based detections using only imagery. However, issues such as false positives need to be corrected in the future. Merging both data sources would allow better results to be achieved.
@inproceedings{soco_21, address = {Bilbao, Spain}, title = {Automatic {Individual} {Tree} {Detection} from {Combination} of {Aerial} {Imagery}, {LiDAR} and {Environment} {Context}}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, isbn = {978-3-030-87869-6}, html = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87869-6_28}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-87869-6_28}, language = {en}, booktitle = {16th {International} {Conference} on {Soft} {Computing} {Models} in {Industrial} and {Environmental} {Applications} ({SOCO} 2021)}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez Pedroche, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, editor = {Sanjurjo González, Hugo and Pastor López, Iker and García Bringas, Pablo and Quintián, Héctor and Corchado, Emilio}, year = {2022}, pages = {294--303}, pdf = {proceedings/amigo_2021_automatic_individual_tree_detection_from_combination_of_aerial_imagery_lidar_and_environment_context.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {SOCO21}, img = {/assets/img/papers/soco21.jpg} } -
 SOCO22
UAV Simulation for Object Detection and 3D Reconstruction Fusing 2D LiDAR and CameraAmigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, Molina, José Manuel, and Lizcano, JorgeIn 17th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2022) Sep 2022
SOCO22
UAV Simulation for Object Detection and 3D Reconstruction Fusing 2D LiDAR and CameraAmigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, Molina, José Manuel, and Lizcano, JorgeIn 17th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2022) Sep 2022Currently it is hard to develop UAV in civil environments, being simulation the best option to develop complex UAV missions with AI. To carry out useful AI training in simulation for real-world use, it is best to do it over a similar environment as the one a real UAV will work, with realistic objects in the scene of interest (buildings, vehicles, structures, etc.). This work aims to detect, reconstruct, and extract metadata from those objects. A UAV mission was developed, which automatically detects all objects in a given area using both simulated camera and 2D LiDAR, and then performs a detailed scan of each object. Later, a reconstruct process will create a 3D model for each one of those objects, along with a geo-referenced information layer that contains the object information. If applied on reality, this mission ease bringing real content to a digital twin, thus improving, and extending the simulation capabilities. Results show great potential even with the current budget specification sensors. Additional post-processing steps could reduce the resulting artefacts in the export of 3D objects. Code, dataset, and details are available on the project page: https://danielamigo.github.io/projects/soco22/
-
 JCS22
Segmentation optimization in trajectory-based ship classificationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelJournal of Computational Science Sep 2022
JCS22
Segmentation optimization in trajectory-based ship classificationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelJournal of Computational Science Sep 2022The paper presents an analysis over eleven trajectory segmentation techniques applied to the study and experimentation of ship classification problems based only on kinematic information. Using the experimental framework introduced in previous works, it cleans, smooths and extracts trajectories from real-world Automatic Identification System (AIS) data. It also applies three balancing solutions to address the lack of an equal distribution among classes. In total, 196 classification experiments have been carried out, which have been presented with a multi-objective analysis to consider the imbalance problem and conflicting metrics (total and minority class accuracies). The results show a Pareto front with different viable solutions for the classification problem, without a dominant one over the rest. The segments generated in the best experiments (Pareto front) are analysed using specific metrics to compare their impact in the classification problem.
@article{jcs22, title = {Segmentation optimization in trajectory-based ship classification}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, issn = {1877-7503}, html = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877750322000096}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2022.101568}, journal = {Journal of Computational Science}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez Pedroche, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, year = {2022}, pages = {101568}, pdf = {articles/amigo_2022_segmentation_optimization_in_trajectory-based_ship_classification.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {JCS22}, img = {/assets/img/papers/jcs22.png} }
2021
-
 SOCO20
Segmentation Optimization in Trajectory-Based Ship ClassificationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 15th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2020) Sep 2021
SOCO20
Segmentation Optimization in Trajectory-Based Ship ClassificationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 15th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2020) Sep 2021An analysis over trajectory segmentation techniques is carried out by the study of the different algorithms and the experimentation over a ship classification problem, which use a data preparation and classification system used in previous works. With the data preparation, the system handles real-world Automatic Identification System (AIS) data, cleaning wrong measurements and smoothening the trajectories by the application of an Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) filter. Also applies some balancing algorithms to address the lack of an equal distribution among classes. To correctly evaluate the classification with the imbalanced data a multiple objective analysis is proposed to consider the minority class and the global accuracy. Over that multi-objective analysis, different segmentation algorithms and its variations are tested to analyze the influence of them into the classification problem. The results show a Pareto front with different viable solutions for the proposed multi-objective problem, without a dominant algorithm over rest of the tested segmentation algorithms.
@inproceedings{amigo_soco_20, address = {Burgos, Spain}, title = {Segmentation {Optimization} in {Trajectory}-{Based} {Ship} {Classification}}, isbn = {978-3-030-57802-2}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-57802-2_52}, language = {en}, booktitle = {15th {International} {Conference} on {Soft} {Computing} {Models} in {Industrial} and {Environmental} {Applications} ({SOCO} 2020)}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, editor = {Herrero, Álvaro and Cambra, Carlos and Urda, Daniel and Sedano, Javier and Quintián, Héctor and Corchado, Emilio}, year = {2021}, pages = {540--549}, pdf = {proceedings/amigo_2020_segmentation_optimization_in_trajectory-based_ship_classification.pdf}, html = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57802-2_52}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {SOCO20}, img = {/assets/img/papers/soco20.png} } -
 FUSION21
Automatic context learning based on 360 imageries triangulation and 3D LiDAR validationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2021 24th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Sep 2021
FUSION21
Automatic context learning based on 360 imageries triangulation and 3D LiDAR validationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2021 24th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Sep 2021Geographic data is very valuable for decision making. There are many hand-adapted datasets of roads or buildings available. However, datasets of other objects are not available, and it is very difficult to generate them manually. Remote sensing can help us to generate datasets of specific objects. This work introduces the main components for an automatic dataset generation process using any kind of sensors. To validate this process, an implementation using an opensource dataset is developed, geolocating traffic barriers using 360-degrees images captured from a car. Its results are validated with the positions extracted from a 3D LiDAR, solving the same problem at a much lower cost, providing an acceptable error for some use cases.
@inproceedings{fusion21_amigo, address = {Rustenburg, South Africa}, title = {Automatic context learning based on 360 imageries triangulation and {3D} {LiDAR} validation}, language = {en}, booktitle = {2021 24th international conference on information fusion ({FUSION})}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez Pedroche, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, year = {2021}, pages = {8}, pdf = {proceedings/amigo_2021_automatic_context_learning_based_on_360_imageries_triangulation_and_3d_lidar_validation.pdf}, doi = {10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9627057}, html = {https://doi.org/10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9627057}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {FUSION21}, img = {/assets/img/papers/fusion21_amigo.png} } -
 FUSION21
Clustering of maritime trajectories with AIS features for context learningSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2021 24th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Sep 2021
FUSION21
Clustering of maritime trajectories with AIS features for context learningSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2021 24th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Sep 2021This paper presents an analysis on Automatic Identification System (AIS) real world ship data to build a system with the capability to extract useful information for an anomaly detection problem. The study focuses on the adjustment of a clustering technique to trajectory data, specifically using a DBSCAN algorithm that is adapted by means of two approaches. On the one hand, the DTW trajectory similarity metric is used to obtain a distance between two trajectories. On the other hand, an extraction of features of interest from each trajectory allowing a summary of the trajectory in a single multidimensional instance. The results show that both approaches are feasible, although not very scalable to larger problems due to the computational complexity of the used algorithms. In addition, the study analyses possible uses of these approaches to existing data mining problems.
@inproceedings{fusion21_sanchez, address = {Rustenburg, South Africa}, title = {Clustering of maritime trajectories with AIS features for context learning}, language = {en}, booktitle = {2021 24th international conference on information fusion ({FUSION})}, author = {Sánchez Pedroche, David and Amigo, Daniel and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, year = {2021}, pages = {8}, pdf = {proceedings/amigo_2021_automatic_context_learning_based_on_360_imageries_triangulation_and_3d_lidar_validation.pdf}, doi = {10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9626956}, html = {https://doi.org/10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9626956}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {FUSION21}, img = {/assets/img/papers/fusion21_sanchez.png} } -
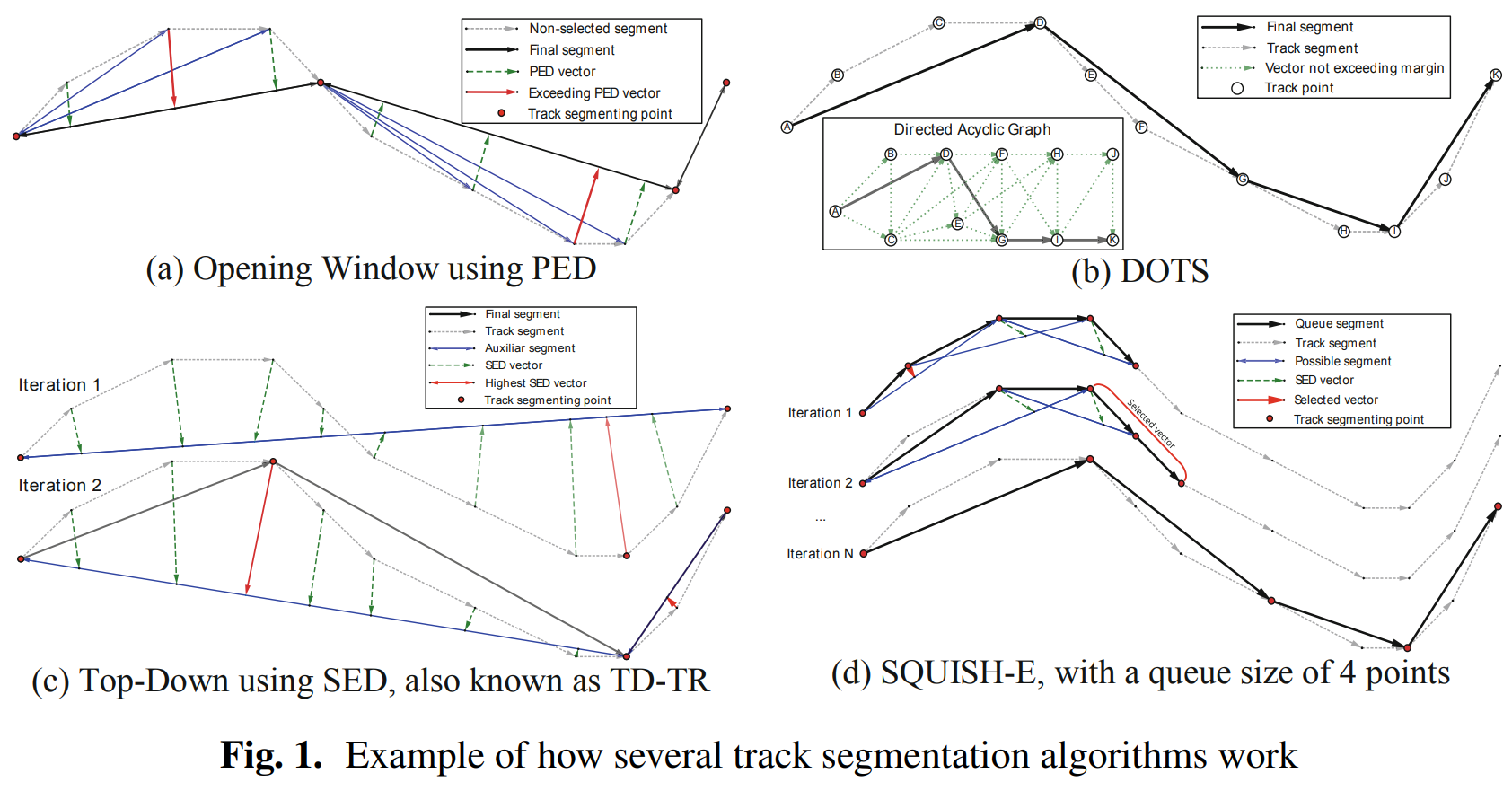
 IJDSN21
Review and classification of trajectory summarisation algorithms: From compression to segmentationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelInternational Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Oct 2021
IJDSN21
Review and classification of trajectory summarisation algorithms: From compression to segmentationAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelInternational Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Oct 2021With the continuous development and cost reduction of positioning and tracking technologies, a large amount of trajectories are being exploited in multiple domains for knowledge extraction. A trajectory is formed by a large number of measurements, where many of them are unnecessary to describe the actual trajectory of the vehicle, or even harmful due to sensor noise. This not only consumes large amounts of memory, but also makes the extracting knowledge process more difficult. Trajectory summarisation techniques can solve this problem, generating a smaller and more manageable representation and even semantic segments. In this comprehensive review, we explain and classify techniques for the summarisation of trajectories according to their search strategy and point evaluation criteria, describing connections with the line simplification problem. We also explain several special concepts in trajectory summarisation problem. Finally, we outline the recent trends and best practices to continue the research in next summarisation algorithms.
@article{ijdsn21, title = {Review and classification of trajectory summarisation algorithms: From compression to segmentation}, volume = {17}, issn = {1550-1477, 1550-1477}, shorttitle = {Review and classification of trajectory summarisation algorithms}, html = {http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/15501477211050729}, doi = {10.1177/15501477211050729}, language = {en}, number = {10}, urldate = {2021-12-14}, journal = {International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez Pedroche, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, month = oct, year = {2021}, pages = {155014772110507}, pdf = {articles/amigo_2021_review_and_classification_of_trajectory_summarisation_algorithms.pdf }, code = {https://danielamigo.github.io/trajectorySummarisationReview}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {IJDSN21}, img = {/assets/img/papers/ijdsn21.png} }
2020
-
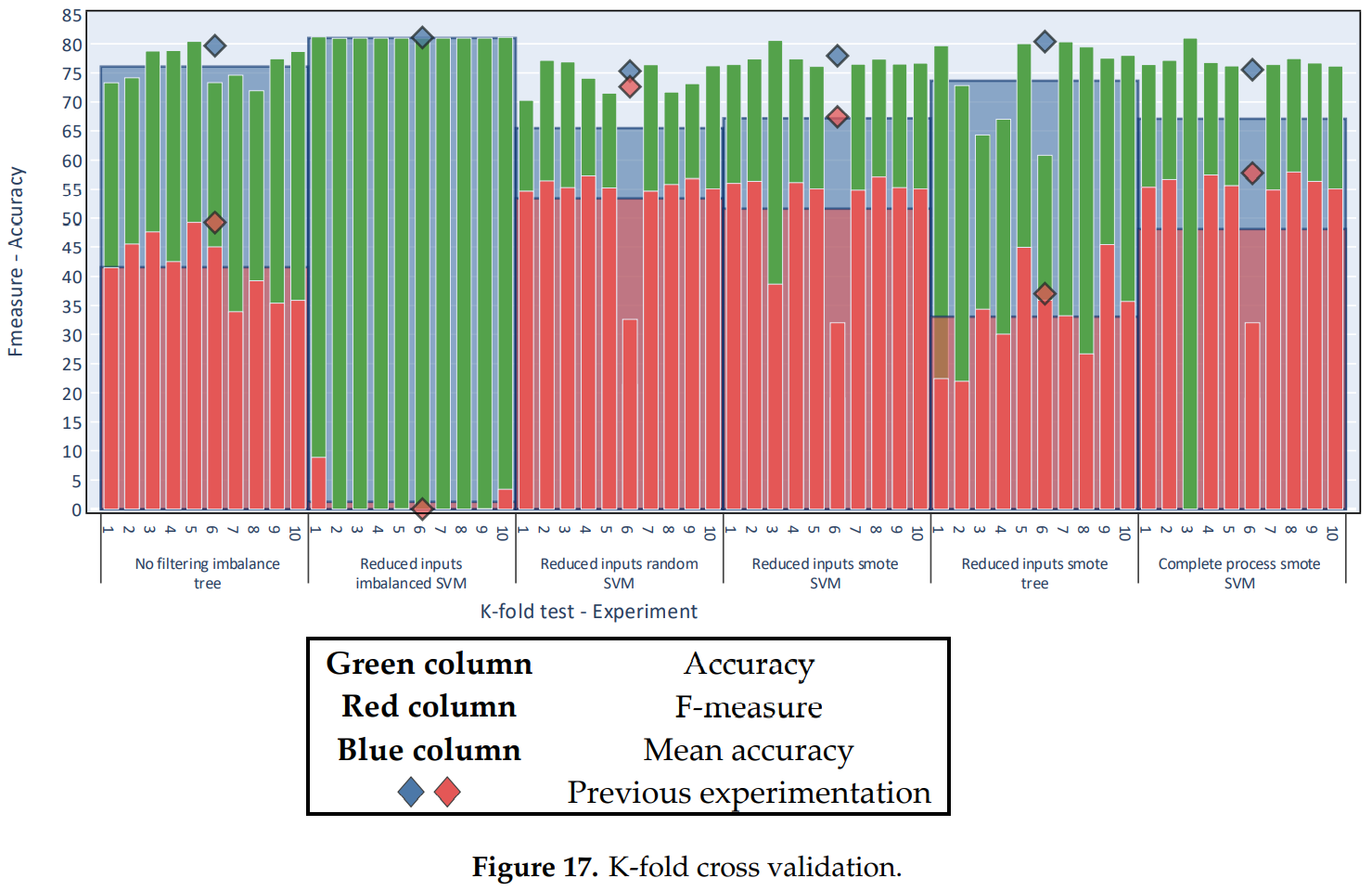 Sensors20
Architecture for Trajectory-Based Fishing Ship Classification with AIS DataSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelSensors Jul 2020
Sensors20
Architecture for Trajectory-Based Fishing Ship Classification with AIS DataSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelSensors Jul 2020This paper proposes a data preparation process for managing real-world kinematic data and detecting fishing vessels. The solution is a binary classification that classifies ship trajectories into either fishing or non-fishing ships. The data used are characterized by the typical problems found in classic data mining applications using real-world data, such as noise and inconsistencies. The two classes are also clearly unbalanced in the data, a problem which is addressed using algorithms that resample the instances. For classification, a series of features are extracted from spatiotemporal data that represent the trajectories of the ships, available from sequences of Automatic Identification System (AIS) reports. These features are proposed for the modelling of ship behavior but, because they do not contain context-related information, the classification can be applied in other scenarios. Experimentation shows that the proposed data preparation process is useful for the presented classification problem. In addition, positive results are obtained using minimal information.
@article{sanchez_sensors_20, title = {Architecture for {Trajectory}-{Based} {Fishing} {Ship} {Classification} with {AIS} {Data}}, volume = {20}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, issn = {1424-8220}, html = {https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/20/13/3782}, doi = {10.3390/s20133782}, language = {en}, number = {13}, urldate = {2020-07-07}, journal = {Sensors}, author = {Sánchez Pedroche, David and Amigo, Daniel and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, month = jul, year = {2020}, pages = {3782}, pdf = {articles/sánchez_pedroche_2020_architecture_for_trajectory-based_fishing_ship_classification_with_ais_data.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {Sensors20}, img = {/assets/img/papers/sensors20.png} }
2019
-
 TFM II
Desarrollo de sistemas de fusión de datos para seguimiento 3DAmigo, DanielJul 2019
TFM II
Desarrollo de sistemas de fusión de datos para seguimiento 3DAmigo, DanielJul 2019La presente tesis está enmarcada en el área de seguimiento y estimación de vehículos. Esta ha ido adquiriendo relevancia a lo largo de los años y ahora, con el auge de vehículos autónomos, aún más. Las técnicas de fusión de datos multisensor mejoran la precisión del seguimiento de los vehículos, mediante la combinación de información de varios sensores sobre un mismo objetivo. Ningún sensor es completamente preciso, cuentan con un ligero error, denominado ruido, que hace que su información no sea completamente fiable. El principal objetivo de la fusión de datos es realizar la estimación más precisa del entorno para utilizar dicha información en una toma de decisiones mejor razonada. Los sistemas de fusión de datos son estructuras muy complejas resultado de la intercomunicación de varios componentes. Existen una gran cantidad de algoritmos para propuestos para cada componente, cada uno con sus ventajas y desventajas en distintos casos. El mejor modo para conocer la mejor configuración de un sistema de fusión es someterlo, en el mismo entorno, a varios algoritmos y determinar cuál es el más adecuado. En esta tesis, tras analizar todo el estado del arte de esta rama, se desarrolla un proyecto de ingeniería para la creación de dos herramientas interactivas con la que facilitar la comparación de sistemas de fusión de datos multisensor. La primera de ellas es la encargada de fijar el entorno en el que probar el sistema, y la segunda, la encargada de realizar las distintas pruebas sobre el entorno y comprobar cuál es la mejor configuración. Las herramientas se desarrollan con éxito cumpliendo la planificación marcada inicialmente. El proyecto abre una línea futura para ampliar la herramienta con más algoritmos de más componentes de fusión de datos, para hacerla más completa.
@thesis{tfm_ii_amigo, title = {Desarrollo de sistemas de fusión de datos para seguimiento {3D}}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, author = {Amigo, Daniel}, year = {2019}, pdf = {theses/amigo_2019_desarrollo_de_sistemas_de_fusión_de_datos_para_seguimiento_3d.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, img = {/assets/img/papers/tfm_ii_amigo.png}, abbr = {TFM II}, school = {Universidad Carlos III de Madrid}, type = {Bachelor Thesis} } -
 TFM CyTI
Técnicas avanzadas de estimación y filtrado: análisis y evaluación en entornos marítimosAmigo, DanielJul 2019
TFM CyTI
Técnicas avanzadas de estimación y filtrado: análisis y evaluación en entornos marítimosAmigo, DanielJul 2019La presente tesis está enmarcada en el área de seguimiento y estimación de vehículos. Esta ha ido adquiriendo relevancia a lo largo de los años y ahora con los vehículos autónomos aún más. Las técnicas de fusión de datos permiten realizar una combinación de información recogida por varias fuentes sobre un mismo objetivo, combinándola y obteniendo de esta manera información de mayor calidad. Estas técnicas aplicadas al área de seguimiento de vehículos tiene como principal objetivo la detección de un entorno cercano. Los sensores instalados en los vehículos tienen un ruido implícito que hace que su información no sea completamente precisa. Gracias a la fusión de datos, obtener una estimación más precisa del entorno hace que la toma de decisiones, ya sea de un vehículo autónomo o de un operario sea más informada y potencialmente más correcta. Los sistemas de fusión de datos son estructuras muy complejas resultado de la intercomunicación de varios sub-sistemas. La estimación de posición es parte de uno de estos sub-sistemas. En esta tesis, tras realizar una gran comprensión del estado del arte de esta rama, se diseña y desarrolla una herramienta que permite la comparación de varias técnicas de estimación de posición. Se implementa las cinco de las técnicas más famosas, así como cálculo de métricas para evaluar su rendimiento y gráficas que le otorguen la capacidad de análisis en un vistazo. El sistema implementado habilita un análisis realizado con varios escenarios escogidos de entorno marítimo. Estos tienen unos resultados positivos, tanto de rendimiento como de consistencia de la estimación. La conclusión de dicho análisis indica que el filtro IMM otorga los mejores resultados.
@thesis{tfm_cyti_amigo, title = {Técnicas avanzadas de estimación y filtrado: análisis y evaluación en entornos marítimos}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, author = {Amigo, Daniel}, year = {2019}, pdf = {theses/amigo_técnicas_avanzadas_de_estimación_y_filtrado.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {TFM CyTI}, img = {/assets/img/papers/tfm_cyti_amigo.png}, school = {Universidad Carlos III de Madrid}, type = {Bachelor Thesis} } -
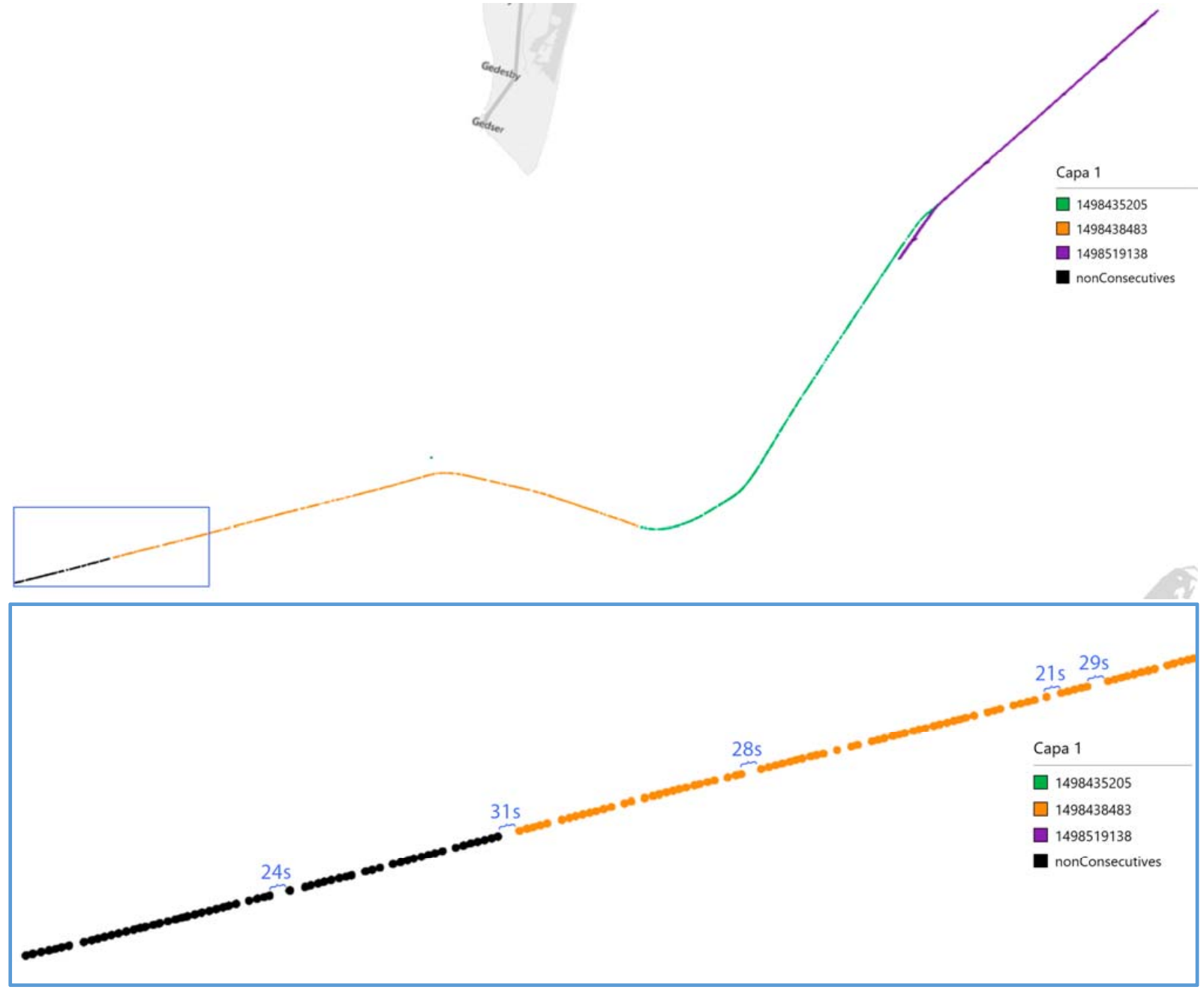 FUSION19
AIS trajectory classification based on IMM dataAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2019 22th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Jul 2019
FUSION19
AIS trajectory classification based on IMM dataAmigo, Daniel, Sánchez Pedroche, David, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 2019 22th international conference on information fusion (FUSION) Jul 2019The importance of the maritime vehicles makes necessary the implementation of systems capable of ensure the safety and security. This paper presents an analysis on Automatic Identification System (AIS) data processed with Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) filter in order to help trajectory data analysis for predictive tasks. The main objective is building a system capable of classifying ships trajectories into different categories as the ship type or the type of activity (fishing, under way with engines, etc.) based on the kinematic and other filter outputs. An automated processing system is implemented to use raw AIS data, preparing and organizing it in order to classify them in ship types and maneuvering state. The appropriate modelling with dynamic models and transition probabilities allow the identification of patterns helpful for trajectory reconstruction and classification. Important aspects as data cleaning, processes parallelization and parameter analysis are dealt on the paper, with results obtained from an available data set.
@inproceedings{amigo_fusion_19, address = {Ottawa, ON, Canada}, title = {{AIS} trajectory classification based on {IMM} data}, booktitle = {2019 22th international conference on information fusion ({FUSION})}, publisher = {IEEE}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Sánchez Pedroche, David and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, month = jul, year = {2019}, pages = {1--8}, html = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9011384}, pdf = {proceedings/amigo_2019_ais_trajectory_classification_based_on_imm_data.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {FUSION19}, img = {/assets/img/papers/fusion19.png} } -
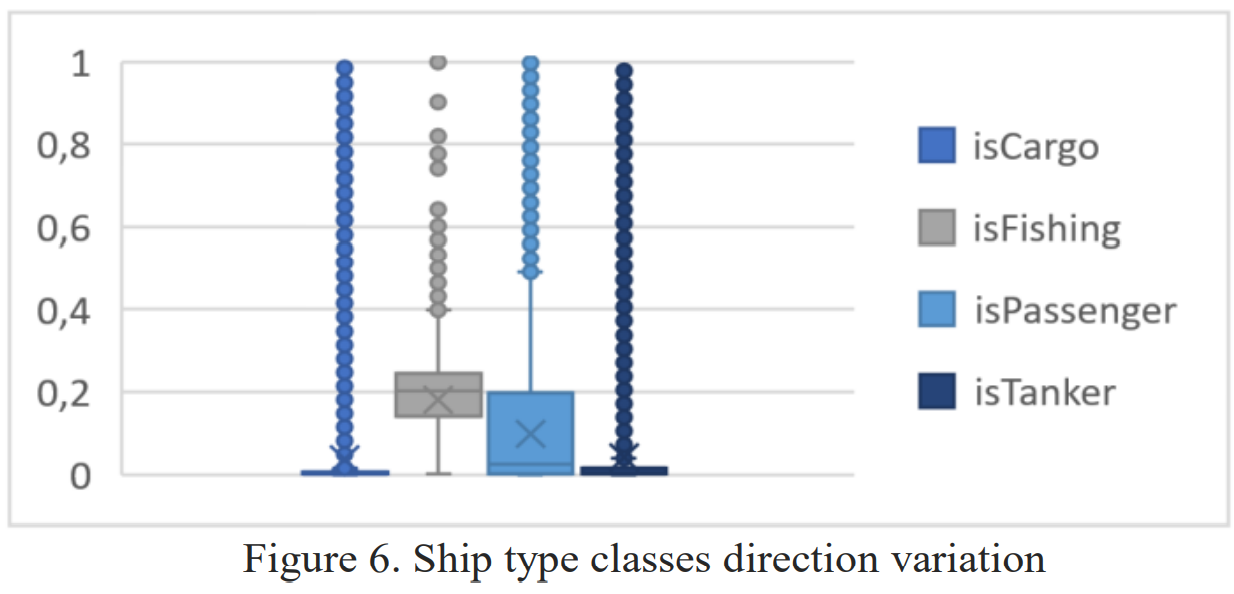 MSAW19
Context information analysis from IMM filtered data classificationSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 1st Maritime Situational Awareness Workshop MSAW Oct 2019
MSAW19
Context information analysis from IMM filtered data classificationSánchez Pedroche, David, Amigo, Daniel, García, Jesús, and Molina, José ManuelIn 1st Maritime Situational Awareness Workshop MSAW Oct 2019On this paper the authors study a set of maritime trajectory classifiers that classify the type of the ship or the kind of movement that is doing. All with the objective of deciding the viability of using the variables set introduced to the algorithm and the classification result as context information useful for a maritime vigilance system that could estimate the ship trajectories with the help of those classification results. To address the classification problem a decision tree and a support vector machine algorithms have been tested and compared. The set of variables to evaluate is obtained from the movement estimation of an Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) filter and its mode probabilities changes. Through the experimentation is evaluated the viability of the problem with the proposed variables, concluding those that could be useful for the proposed problem.
@inproceedings{sanchez_msaw_19, address = {Lerici, Italy}, title = {Context information analysis from {IMM} filtered data classification}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, language = {en}, booktitle = {1st {Maritime} {Situational} {Awareness} {Workshop} {MSAW}}, author = {Sánchez Pedroche, David and Amigo, Daniel and García, Jesús and Molina, José Manuel}, month = oct, year = {2019}, pdf = {proceedings/sánchez_pedroche_2019_context_information_analysis_from_imm_filtered_data_classification.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, abbr = {MSAW19}, img = {/assets/img/papers/msaw19.png} }
2017
-
 TFG
Diseño y desarrollo de un sistema domótica sobre plataforma AndroidAmigo, Daniel, and Patricio Guisado, Miguel ÁngelOct 2017
TFG
Diseño y desarrollo de un sistema domótica sobre plataforma AndroidAmigo, Daniel, and Patricio Guisado, Miguel ÁngelOct 2017El sector de la domótica está creciendo mucho en los últimos años. Es un área muy grande en la que hay mucho por explorar ahora que se cuenta con una tecnología más que preparada para ello. Además de las ventajas físicas que conllevan, la seguridad y el ahorro energético que ofrecen está más que demostrado. Por otro lado, tenemos los dispositivos móviles o smartphones, que hace diez años no existían y se han arraigado a la sociedad actual de una manera nunca antes vista. No se concibe una sociedad sin ellos, todos tenemos mínimo un dispositivo inteligente. Si unimos ambos conceptos, tenemos una aplicación para dispositivos móviles (Android en nuestro caso), capaz de controlar los dispositivos domóticos. Pero existe un problema, este concepto ya existe, controlando dispositivos de todo tipo. Pero, como se verá a lo largo del documento, estas soluciones cuentan con dispositivos de altísimo coste para su funcionalidad. En este proyecto nos vamos a enfocar en un ámbito más genérico que dispositivos fijos, trabajando con la tecnología Arduino, dando soporte a todo tipo de dispositivos, al poderse programar para realizar cualquier acción. Además, esta solución implica otro beneficio más, puesto que los dispositivos Arduino interactúan con la aplicación vía WiFi, abarcando el concepto de IoT y dando una solución práctica y de calidad a las personas que busquen un sistema domótico inalámbrico de bajo presupuesto, algo que no existe en el mundo.
@thesis{tfg_amigo, title = {Diseño y desarrollo de un sistema domótica sobre plataforma {Android}}, copyright = {All rights reserved}, language = {es}, author = {Amigo, Daniel and Patricio Guisado, Miguel Ángel}, year = {2017}, pages = {185}, pdf = {theses/amigo_2017_diseño_y_desarrollo_de_un_sistema_domótica_sobre_plataforma_android.pdf}, bibtex_show = {true}, img = {/assets/img/papers/tfg_amigo.png}, abbr = {TFG}, school = {Universidad Carlos III de Madrid}, type = {Bachelor Thesis} }